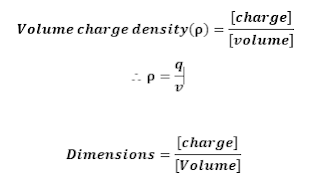Monday, January 3, 2022
Friday, January 10, 2020
What is the work energy theorem?
Hi, Work energy theorem is one of the fundamental theorem in
physics. Simply it is a relation between work and kinetic energy of a body.
Then a question arises that what is the work energy theorem is all
about and how we can understand it.
It is extremely easy to understand. We can understand it in
a simple manner. For this sake of purpose; let we study the complete derivation
or proof of work energy theorem.
Equation of work energy theorem
We derive the work energy theorem by following the equation
of work.
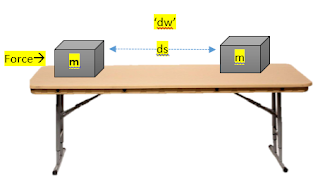
Let we consider in general;
an object of mass ‘m’ is applied by
a force ‘f’ which displaced it by a displacement ‘s’
Then amount of work done will be
given by the equation of work.
Hence;
work= force x displacement w=f x s
work= force x displacement w=f x s
Saturday, January 4, 2020
What is meant by continuous charge distribution?
Hi, To this very beautiful question i tried to write a humble answer. Let we discuss Continuous charge distribution and what does actually it mean. Before we should put ourselves in topic; i think we must take a brief view of charges and their behaviour.
Charge: It is the property of material body due to which it apply a force on another body near to it. The force may be of type of attraction or repulsion. The charges are categories into two types namely:-
1 Positive(+)
2 Negative(-)
If a body or object has no charge i.e. it is neither positive nor negative then it is considered as neutral ( charge less).
According to the coulomb law if two like charges(positive and positive or negative and negative) are close to each other they apply the force of repulsion on each other. Whereas if charges are unlike then they apply force of attraction on each other. For more detail we can learn coulombs law also but for now we restrict ourselves to Continuous charge distribution.
Uniform charge distribution:
The charge is not accumulated in some part but is spread uniformly; it is called as uniform charge distribution.
Non-Uniform charge distribution:
The shape of conductor is irregular; charges distribution will not be the same. More charges will accumulated at various points; at the curves and sharp points the value of charges will not be same. It is called as Non-Uniform charge distribution.
Concept of charge density:
The charge can be distributed over any body of any shape. The distribution of charge may be uniform or non uniform.


If
the conductor is in sphere shape the charge per unit volume is called as volume
charge density.
Charge: It is the property of material body due to which it apply a force on another body near to it. The force may be of type of attraction or repulsion. The charges are categories into two types namely:-
1 Positive(+)
2 Negative(-)
If a body or object has no charge i.e. it is neither positive nor negative then it is considered as neutral ( charge less).
According to the coulomb law if two like charges(positive and positive or negative and negative) are close to each other they apply the force of repulsion on each other. Whereas if charges are unlike then they apply force of attraction on each other. For more detail we can learn coulombs law also but for now we restrict ourselves to Continuous charge distribution.
Uniform charge distribution:
The charge is not accumulated in some part but is spread uniformly; it is called as uniform charge distribution.
Non-Uniform charge distribution:
The shape of conductor is irregular; charges distribution will not be the same. More charges will accumulated at various points; at the curves and sharp points the value of charges will not be same. It is called as Non-Uniform charge distribution.
Concept of charge density:
The charge can be distributed over any body of any shape. The distribution of charge may be uniform or non uniform.
If the body on which charge is being distributed is of perfect shape then distribution of charges becomes uniform.Depending upon the geometry(shape) of conductor the concept of charge density get divided into three types.
1. Linear Charge density(λ)
2. Surface Charge density(σ)
3. Volume Charge density(ρ)
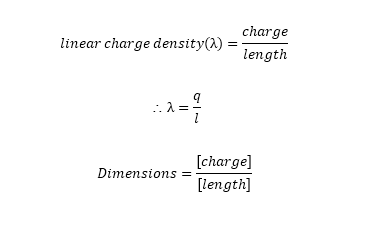
a] Linear Charge density(λ):
If the conductor is in linear shape then charges per unit length is called as linear charge density().
If the conductor is in linear shape then charges per unit length is called as linear charge density().
Consider ‘L’ be the length of
conductor.
‘q’ be the amount of charges given to conductor.
Hence, Linear charge density is given by;
(Linear charge density formula)

S.I. unit for linear charge density : Coulomb/metre
[λ]= [M0 L-1 T1
I1]
b] Surface charge density(σ):
If the conductor is in rectangular shape
the charge per unit area is called as surface charge density.
Let us consider; ‘A’ be the area of
conductor,
‘q’ be the amount of charges given to conductor.
Hence, surface charge density is given
by;
(Surface charge density formula)

S.I. unit for surface charge density : Coulomb/metre2
[σ] = [M0 L-2T1 I1]
c] Volume
charge density(ρ):
Let
we consider, ‘V’ be the volume of conductor,
‘q’ be the amount of charges
given to conductor.
Hence,
Volume charge density is given by;
(Volume charge density formula)
S.I.
unit for Volume charge density : Coulomb/metre3
[ρ]= [M0 L-3T1 I1]
Friday, January 3, 2020
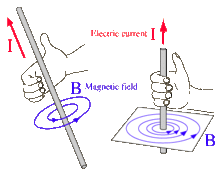
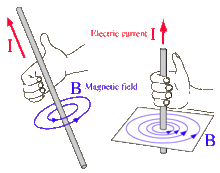
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current-Part 2
Hi, as we already studied the magnetic effect of electric current; the many question arises that who discovered it? What is Oersted law and so many others? Beyond the concern with class 10 magnetic effect of electric current notes we further take our discussion to depth level.
When I think about Oersted law; it is so common thing that if two bodies are experiencing the force from each other it surely means that there must be a some strong connection or similarities or even strong dissimilarities between forces.
The Oersted law gives the idea about force acting on conductor carrying current when it get placed in external magnetic field.
The Oersted law gives the idea about force acting on conductor carrying current when it get placed in external magnetic field.
Before I lead to the Oersted law. I like to ask you don’t you see the answer hidden in question itself.
I think yes. Still let us discuss something about simple and beautiful answer to this interesting question.
I have a simple imagination.
Let we consider a current carrying conductor; which is placed in uniform magnetic field. Then we observe that the conductor is experiencing a force. Here is the magic comes.
Why it should happen? Why conductor should acted by a force in magnetic field. The magnetic force is acting on conductor but to counter it there must be a force due to conductor. Which must be similar to magnetic force. Hence it is clear that current produces the magnetic field in conductor and which counter the force due to magnetic field.
This is the basic idea of Oersted law.
The magnetism produced by the flow of an electric current. This idea was studies by Danish scientist named Oersted in year 1820.
There he studied that if an electric current is sent through a conductor which is placed in uniform magnetic field. The conductor experiences a force due to the field. This is what we studied in Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Class 10 Notes.
We can define the magnetic effect of electric current in simple way.
The phenomenon of production of magnetism due to the flow of electric current is called as magnetic effect of electric current.
The above observation can be diagrammatically put as;
Say,
‘L’ be the length of conductor
‘I’ be the value of current
‘B ‘ be the magnetic induction
According to Oersted the force is given by;
In scalar form; it can be written as;
Where angle 'Ɵ'
is in between the length and direction of magnetic induction(B).
Now; a question must arise that why conductor experience the force when get placed in magnetic field of induction (B).
This clearly means that to relate with the external magnetic field there must be some another magnetic field to be in part for the force and that field is around the conductor which is generated by flow of electric current.
This concept of production of magnetic field around a conductor due to flow of electric current known as magnetic effect of electric current.
The value of force is maximum for angle
Ɵ=90 °
Ɵ=90 °
F=ILBSin90 °= ILB
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Class 10 Notes
Electricity and magnetism both are symmetric. This concept is one of the fundamental concept in electromagnetism. MEEC has impact on study of physics. Further we study the Oersted law. In this article Magnetic effect of electric current class 10 notes will be in focus.
An electric current carrying conductor like wire behaves
like a magnet. Both electricity and magnetism are linked with each other. For
example compass needle get deflected by electric current through a conductor.
It clearly proves that the magnetism produced due to the flow of electric
current.
The concept where magnetism produced due to the flow of electric current through the conductor is called as magnetic effect of electric current.
Here in this section we will discuss about the magnetism or magnetic effect. I would clearly say that the magnetism produced by the flow of an electric current. This idea was studies by Danish scientist named Oersted in year 1820. There he studied that if an electric current is sent through a conductor which is placed in uniform magnetic field. The conductor experiences a force due to the field.
Physics and Math Tutor
Physics and Math Tutor: It serves for students at free. It brilliantly explains exam questions into topics. Gives you a wonderful idea. Sample question papers, marking schemes, previous year question papers, solved question papers, Revise A-levels papers, revision notes, worksheets and helpful solution banks.
Powered by Blogger.
About Me
Sweepstakes2021
Wedding registration Baby Registry