Hi, To this very beautiful question i tried to write a humble answer. Let we discuss Continuous charge distribution and what does actually it mean. Before we should put ourselves in topic; i think we must take a brief view of charges and their behaviour.
Charge: It is the property of material body due to which it apply a force on another body near to it. The force may be of type of attraction or repulsion. The charges are categories into two types namely:-
1 Positive(+)
2 Negative(-)
If a body or object has no charge i.e. it is neither positive nor negative then it is considered as neutral ( charge less).
According to the coulomb law if two like charges(positive and positive or negative and negative) are close to each other they apply the force of repulsion on each other. Whereas if charges are unlike then they apply force of attraction on each other. For more detail we can learn coulombs law also but for now we restrict ourselves to Continuous charge distribution.
Uniform charge distribution:
The charge is not accumulated in some part but is spread uniformly; it is called as uniform charge distribution.
Non-Uniform charge distribution:
The shape of conductor is irregular; charges distribution will not be the same. More charges will accumulated at various points; at the curves and sharp points the value of charges will not be same. It is called as Non-Uniform charge distribution.
Concept of charge density:
The charge can be distributed over any body of any shape. The distribution of charge may be uniform or non uniform.


If
the conductor is in sphere shape the charge per unit volume is called as volume
charge density.
Charge: It is the property of material body due to which it apply a force on another body near to it. The force may be of type of attraction or repulsion. The charges are categories into two types namely:-
1 Positive(+)
2 Negative(-)
If a body or object has no charge i.e. it is neither positive nor negative then it is considered as neutral ( charge less).
According to the coulomb law if two like charges(positive and positive or negative and negative) are close to each other they apply the force of repulsion on each other. Whereas if charges are unlike then they apply force of attraction on each other. For more detail we can learn coulombs law also but for now we restrict ourselves to Continuous charge distribution.
Uniform charge distribution:
The charge is not accumulated in some part but is spread uniformly; it is called as uniform charge distribution.
Non-Uniform charge distribution:
The shape of conductor is irregular; charges distribution will not be the same. More charges will accumulated at various points; at the curves and sharp points the value of charges will not be same. It is called as Non-Uniform charge distribution.
Concept of charge density:
The charge can be distributed over any body of any shape. The distribution of charge may be uniform or non uniform.
If the body on which charge is being distributed is of perfect shape then distribution of charges becomes uniform.Depending upon the geometry(shape) of conductor the concept of charge density get divided into three types.
1. Linear Charge density(λ)
2. Surface Charge density(σ)
3. Volume Charge density(ρ)
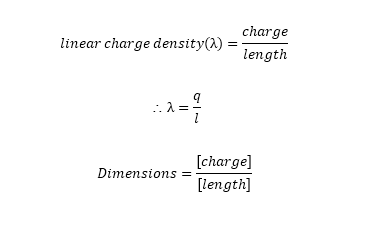
a] Linear Charge density(λ):
If the conductor is in linear shape then charges per unit length is called as linear charge density().
If the conductor is in linear shape then charges per unit length is called as linear charge density().
Consider ‘L’ be the length of
conductor.
‘q’ be the amount of charges given to conductor.
Hence, Linear charge density is given by;
(Linear charge density formula)

S.I. unit for linear charge density : Coulomb/metre
[λ]= [M0 L-1 T1
I1]
b] Surface charge density(σ):
If the conductor is in rectangular shape
the charge per unit area is called as surface charge density.
Let us consider; ‘A’ be the area of
conductor,
‘q’ be the amount of charges given to conductor.
Hence, surface charge density is given
by;
(Surface charge density formula)

S.I. unit for surface charge density : Coulomb/metre2
[σ] = [M0 L-2T1 I1]
c] Volume
charge density(ρ):
Let
we consider, ‘V’ be the volume of conductor,
‘q’ be the amount of charges
given to conductor.
Hence,
Volume charge density is given by;
(Volume charge density formula)
Conclusions:In this article of Physics and math tutor; the distribution of charges has been discussed in form of continuous charge distribution. Further its three types also has been explained. The above information might not cover all the aspects of the topic but still we genuinely tried to put a better idea of the concept.


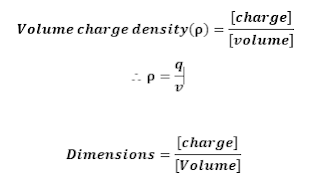



Nice description in detail.
ReplyDelete